| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- string
- kotlin
- Github
- JUnit
- db
- 토비의 스프링
- Action
- 사이드 프로젝트
- AOP
- mutable
- template
- git
- 알고리즘
- Spring
- QueryDSL
- compiler
- EC2
- Airflow
- aws
- immutable
- workflow
- rds
- redis
- springboot
- JPA
- CodeDeploy
- build_test
- java
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발 일기
프로그래머스 레벨3 가장 먼 노드 (JAVA) 본문
저번 게임 맵 최단거리에 이어 바로 풀어버린
프로그래머스 레벨3 가장 먼 노드!
BFS 로 풀었다!
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49189
코딩테스트 연습 - 가장 먼 노드
6 [[3, 6], [4, 3], [3, 2], [1, 3], [1, 2], [2, 4], [5, 2]] 3
programmers.co.kr
모든 코드는 GitHub 에 올려놓았다.
이건 풀이가 2개 있다 내가 처음 푼 풀이와
조언을 받은 풀이
일단 처음 푼 풀이부터 보자.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
int[] countArr = new int[n + 1];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(1);
countArr[1] = 1;
int max = 0;
visited[1] = true; // 본인 방문처리
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int x = queue.poll();
int nodeCount = countArr[x]; // 1 과 거리
// max 치 확인
if (nodeCount > max) {
max = nodeCount;
answer = 1; //초기화 최대값 변경으로
} else if (nodeCount == max) {
answer++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < edge.length; i++) {
if (edge[i][0] == x) { // 노드값이 현재 노드와 같은지..
int node = edge[i][1];
if (!visited[node]) { //미방문
queue.add(node); // 값추가
countArr[node] = nodeCount + 1;
visited[node] = true; // 본인 방문처리
}
} else if (edge[i][1] == x) {
int node = edge[i][0];
if (!visited[node]) { //미방문
queue.add(node); // 값추가
countArr[node] = nodeCount + 1;
visited[node] = true; // 본인 방문처리
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
BFS로 0,0부터 노드를 차례차례 탐색해하고
edge의 위치가 바뀐 것도 탐색해서 추가해주었다.
바뀐 것도 추가로 else if로 탐색하는 이유는
{2,4}, {5,2} 이런 식으로 표현이 되어있는 것도 있기에 2번 노드랑 관련된
edge의 모든 거를 탐색해주어야 한다.
하지만 이렇게 풀면
시간 복잡도가 O(NE)가 되어버린다.

보는 거처럼 7,8,9 테스트 케이스의 시간이 어마어마 해 진다.
지인의 조언을 받아
간선을 미리 정리하고 풀어보았다 이경우에는
시간 복잡도가 O(N+E)가 된다고 한다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n);
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for(int i=0; i<edge.length; i++) {
graph.get(edge[i][0]).add(edge[i][1]);
graph.get(edge[i][1]).add(edge[i][0]);
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
int[] countArr = new int[n + 1];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(1);
countArr[1] = 1;
int max = 0;
visited[1] = true; // 본인 방문처리
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int x = queue.poll();
int nodeCount = countArr[x]; // 1 과 거리
// max 치 확인
if(nodeCount > max) {
max = nodeCount;
answer = 1; //초기화 최대값 변경으로
} else if(nodeCount == max) {
answer++;
}
for(int i=0; i<graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int node = graph.get(x).get(i);
if(!visited[node]) {
queue.add(node);
countArr[node] = nodeCount +1;
visited[node] = true;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
미리 간선을 전 처리해주고 탐색을 시작하였다.
시간은 정말 놀라울 정도였다
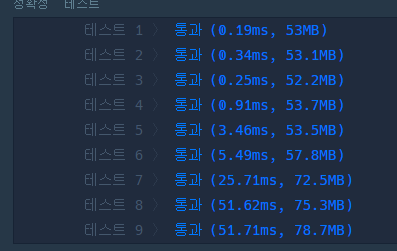
진짜 놀라웠다.
새로운 경험을 했다 앞으로 전처리에 관해서도 신경을 쓸 수 있도록
기억해 두어야겠다.
'알고리즘 > programmers' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 예상 대진표 (JAVA) (0) | 2021.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 배달 (JAVA) (0) | 2021.07.31 |
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 게임 맵 최단거리 (0) | 2021.07.20 |
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 피보나치의 수 (JAVA) (0) | 2021.07.20 |
| 프로그래머스 레벨2 다음 큰 숫자 (JAVA) (0) | 2021.07.20 |




